
General Considerations on Ex Hazardous Area Inspections
Legal/Regulatory: Required by ATEX 1999/92/EC (ATEX Workplace Directive) and IEC 60079-17 (inspection and maintenance of Ex installations).
Competence: Must be carried out by personnel with Ex competence (CompEx, IECEx CoPC, national schemes).
Inspection Types: Initial (before energisation/takeover) // Periodic (routine, detailed, sample-based) // Continuous (condition-based, after maintenance/repair)
Documentation: Clear records of conformity, nonconformities, remedial actions.
Risk-based: Inspection intervals and depth depend on zone, equipment EPL, risk of deterioration.
Pros and Cons of Ex Inspections
Pros
Safety: Reduces ignition risk → prevents explosions. Compliance: Demonstrates fulfilment of ATEX/IECEx and national regulations.
Reliability: Early detection of damage (corrosion, cable issues, loose glands).
Asset integrity: Protects long-term value and availability of plant.
Insurance & liability: Proof of diligence lowers liability exposure.
Knowledge feedback: Provides lessons for design improvements.
Cons
Cost: Skilled inspectors, downtime, travel.
Disruption: Shutdowns or restricted access during inspections.
Human factor: Subjectivity in visual assessments if not standardized.
Documentation burden: High volume of reports, records, follow-ups.
Sample vs 100% inspection: Risk of missing hidden defects if sampling only.
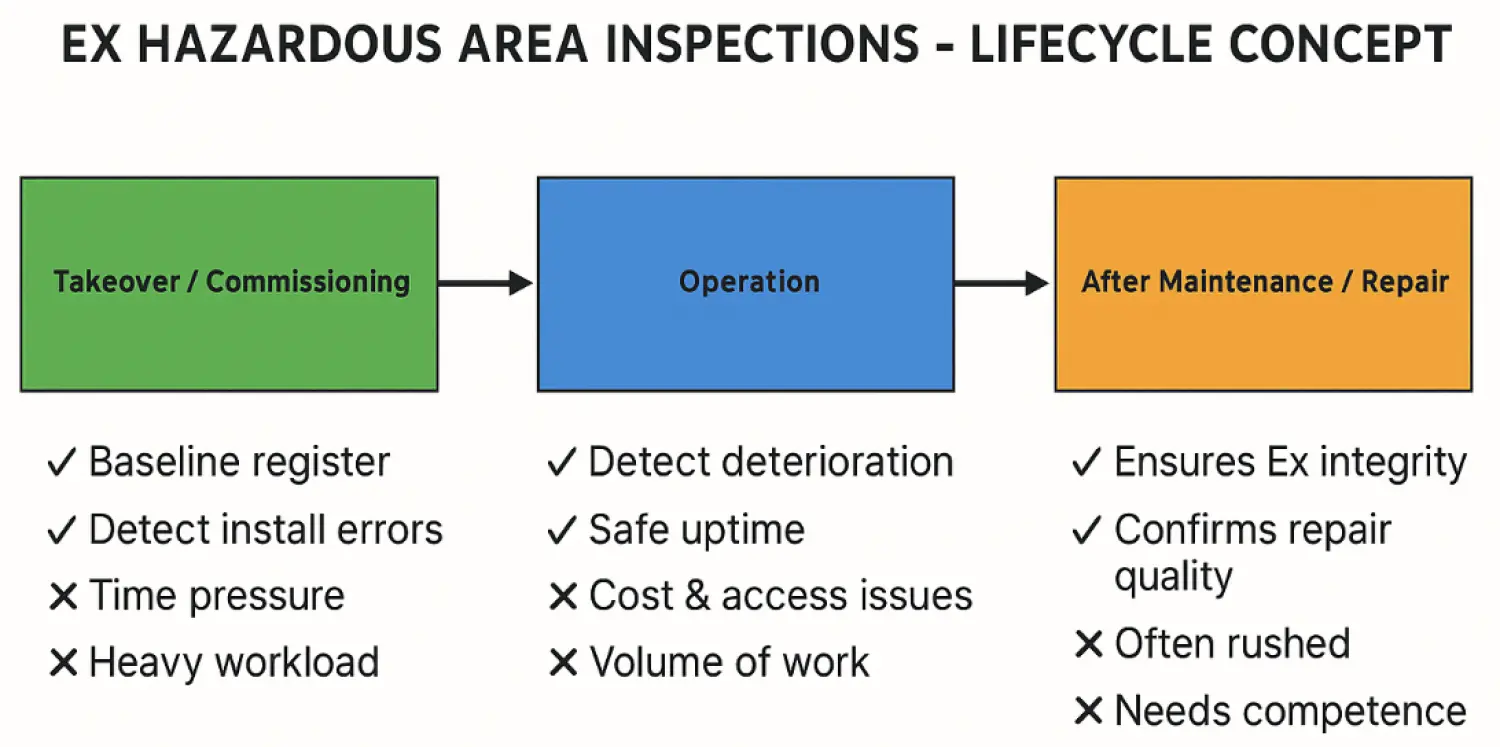
Lifecycle Differentiation
(A) Takeover / Initial Commissioning
Focus: Conformity check against design, drawings, Ex certificates.
Pros: Baseline established (as-built records). Detects installation errors before energisation (wrong glands, missing IP seals, uncertified components).
Cons: High workload in short time. Pressure from project deadlines → risk of "rubber stamp" inspections.
Outcome: Inspection certificate of conformity / Ex register baseline.
(B) Operation Phase
Focus: Periodic inspections (visual/close/detailed).
Pros: Detects wear, corrosion, cable degradation. Allows risk-based maintenance planning.
Cons: Access to live equipment can be limited (hot work permits, shutdowns). Potentially expensive to maintain full compliance across large sites.
Outcome: Ongoing Ex register with updated inspection status.
(C) After Maintenance / Repair / Modification
Focus: Verification of repair and reinstallation.
Pros: Confirms that intervention hasn't compromised Ex protection (e.g. incorrect gasket, improper torque, lost IP rating). Ensures Ex repair workshop certification (IEC 60079-19).
Cons: Often overlooked or rushed. Requires detailed knowledge of repair standards, not just inspection checklists.
Outcome: Updated record, confirmation that repaired equipment is still compliant before return to service.
In short:
At takeover: inspections are preventive and baseline-setting.
In operation: inspections are predictive and condition-based.
After repair: inspections are corrective and assurance-focused.
Keep up good work!
Note: Your comment will only appear on the site after review. Your email address will not be visible, only your name and comment.